 4 minutes read
4 minutes readAre you still hitting the Run button every time you want to verify a GUI element in your Python Qt and QML application looks as you expected?
Or are you relying on your working memory to imagine the changes in your mind?
Both approaches work, but you are wasting a lot of time and energy, which you could spend more productive on coding.
In this article, you will learn about an approach called live coding which I frequently use during GUI development with Qt QML.
The idea is to shorten feedback loops by automatically reloading the GUI whenever you change the source code.
Additionally, we combine the automatic reloading with prototype or playground UIs, where you can work on parts of the UI in an isolated manner.
I see live coding as the GUI counterpart to test-driven development for normal source code. It's all about more consistent development speed thanks to shorter feedback loops. In fact, TDD and live-coding are a great combination when working with Python Qt and QML.
Live coding for QML applications is nothing I have invented. There is also the now official QmlLive Bench. However, so far it only supports Qt/C++ applications.
Moreover, I noticed that for bigger projects you need to write your own live coding environment anyway. For example, I also added live coding to QtQuickVcp as demonstrated in this video.
Components
The live coding environment is fairly simple. In fact, it's so simple that you can easily implement it for each of your projects. It consists of the following software components:
- FileWatcher: Watches your file system for changes and sends out notification signals.
- ModuleLoader: Searches a directory tree for Python QML modules to load.
- PythonReloader: Restarts the whole application to re-register alls Python QML modules.
- ProjectBrowser: Lists all QML files in a directory tree.
- QML Loader: This is the Loader component provided by Qt. It enables users to load and reload QML code at run-time.
With these few simple components, we can easily build our own small live coding environment. Additionally, we may have some code handle errors attached to sys.excepthook plus a small GUI.
How does it work
The concept is as simple as it is powerful.
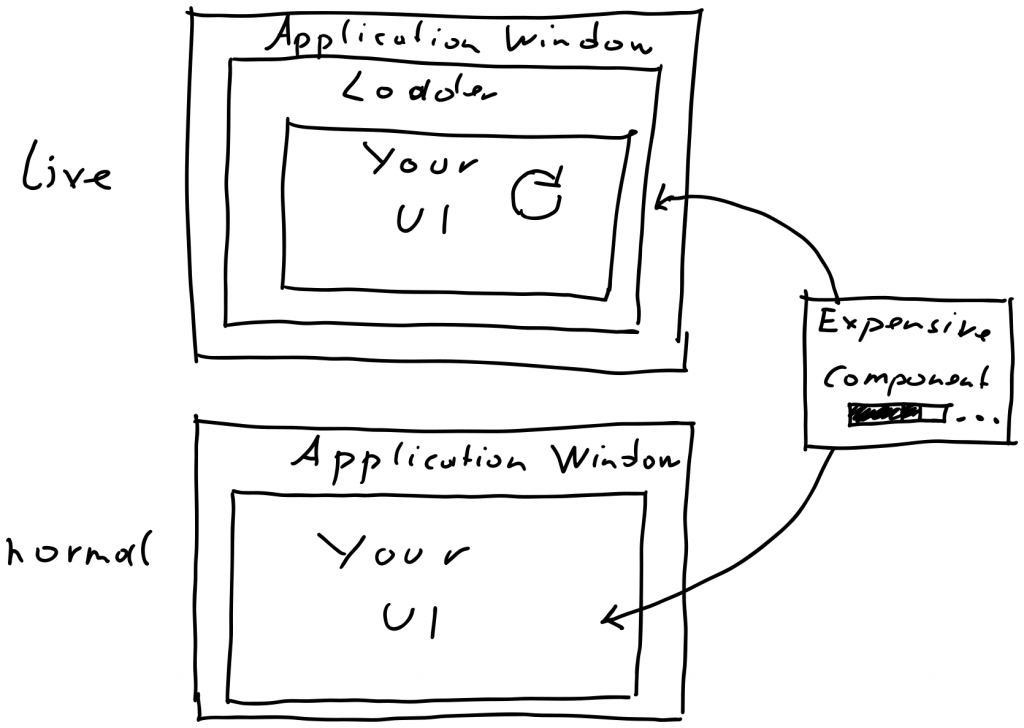
Instead of loading our GUI application as normal, we inject the QML part of our live coding environment between the top level window and our GUI code.
Live Coding QML applications
For production, we can use our GUI code as usual, for development we use the live coding environment.
Sometimes we have resources or loading-time expensive components. For example a 3D simulation window. We can place these components outside of our live coding environment to speed up loading time.
Structuring the Code
When working with Python and QML we have GUI code written int the QML language and business logic written in Python.
Our business logic code is loaded into the GUI as QML component as part of QML module. A QML module is the equivalent of a Python module, but for QML.
A QML module may contain both, QML code and Python code. Therefore, it makes sense to let the Python and QML code live together in a single directory.
For example, a QML module providing logic and GUI representation of a file system browser may look as follows:
- [filesystem]
- qmldir
- __init__.py
- file_system_tree_model.py
- FileSystemTreeView.qml
The qmldir file registers the QML components into QML module. The __init__.py file does the same for the Python QML components.
To discover Python QML module, the __init__.py contains a register_qml_types method.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PyQt5.QtQml import qmlRegisterType
from .file_system_tree_model import FileSystemTreeModel
MODULE_NAME = 'filesystem'
def register_types():
qmlRegisterType(FileSystemTreeModel, MODULE_NAME, 1, 0, FileSystemTreeModel.__name__)
This makes it easy for our ModuleLoader to automatically find and register any QML Python modules.
The Python Qt Live Coding Environment
To make our life as HMI engineers easier, I created a Python Qt live coding environment that comes with all the required parts to start hacking on a Python QML GUI.
You can find the project on GitHub: python-qt-live-coding
Python Qt Live Coding Environemnt
pip install python-qt-live-coding
The live coding environment comes with a live runner which enables you to live
code Qt GUIs quickly.
Run following to test drive the example:
python_qt_live_coding examples
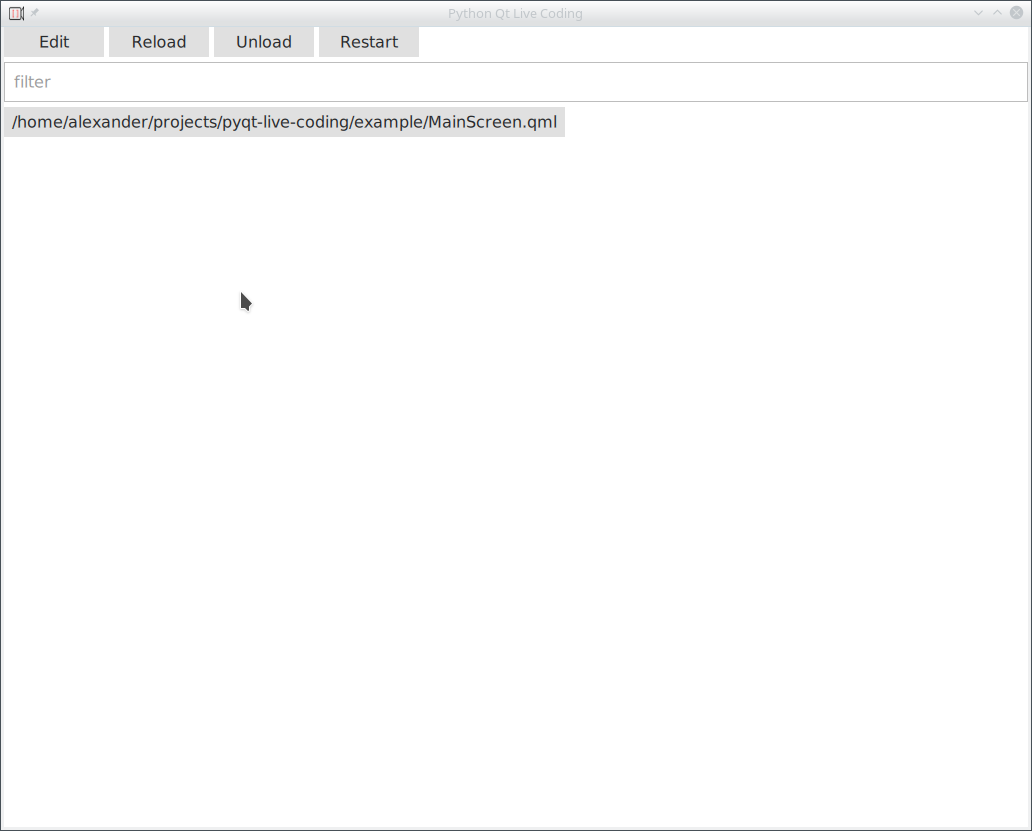
You will instantly see the example project in the live runner.
Live Runner Example
Now you can either select the MainScreen.qml file or type MainScreen in the filter.
When you type, the file will be automatically selected.
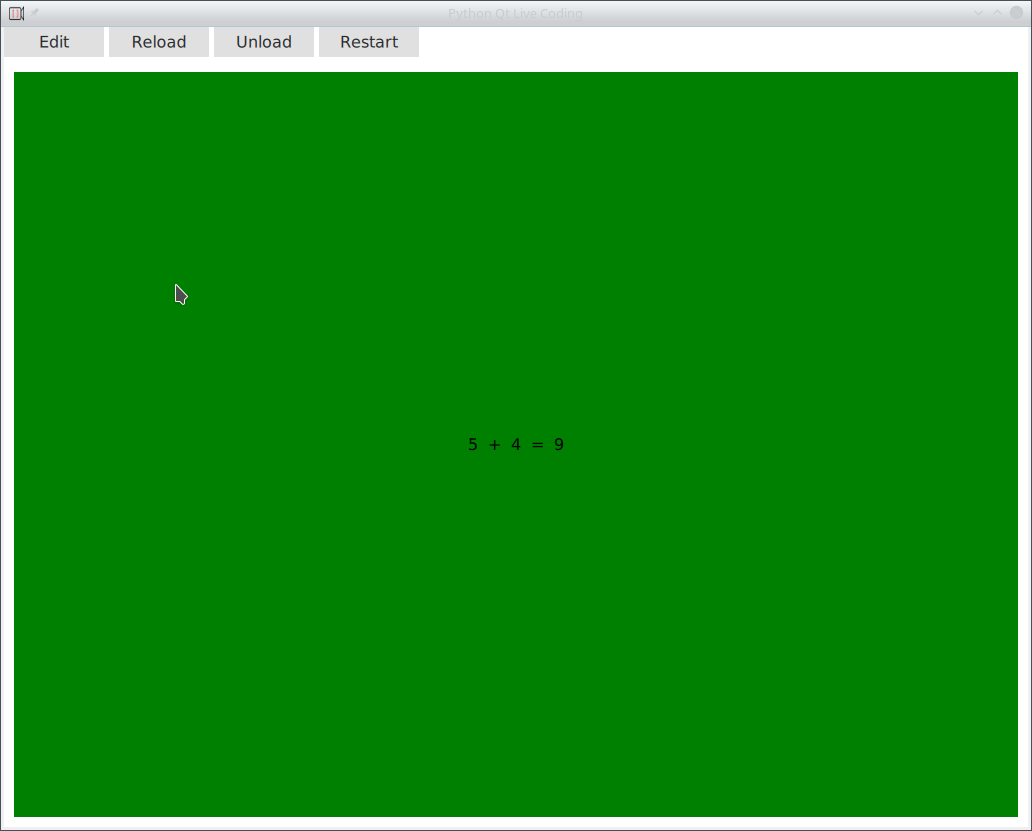
When loaded you will see following.
Live Coding Example 2
This is the example GUI inside the live runner.
Now press the Edit button. Your favorite text editor should open promptly.
Edit the code inside the editor and you will see the GUI updates instantly when you save the document.
Conclusion
Live coding is a great concept that can be applied to Python Qt and QML applications.
The python-qt-live-coding project brings you everything you need in a box.
Additionally, it can be used as a base for a custom live-coding environment for your application.
If you want to see another example that integrates QML with Python, check out this GitHub repository.
Happy coding!
Your Machine Koder